in this article and in the next article you will learn about memory and addresses of a memory location , in which information, data, are store
The Design of a Memory Chip
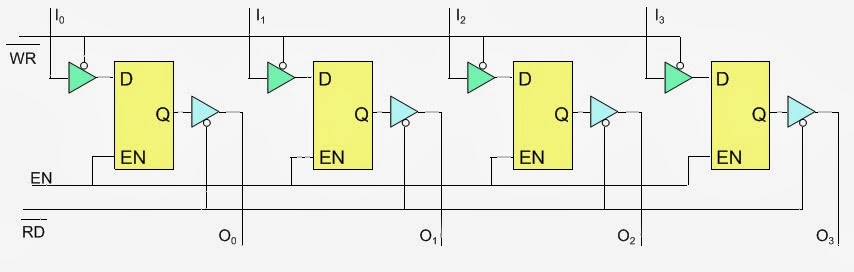
Using the RD and WR controls we can determine the direction of flow either into or out of memory. Then using the appropriate Enable input we enable an individual memory register.
What we have just designed is a memory with 4 locations and each location has 4 elements (bits). This memory would be called 4 X 4 [Number of location X number of bits per location].
The Enable Inputs
How do we produce these enable line?
Since we can never have more than one of these enables active at the same time, we can have them encoded to reduce the number of lines coming into the chip.
These encoded lines are the address lines for memory.
The Design of a Memory Chip
So, the previous diagram would now look like the following:
The Design of a Memory Chip
Since we have tri-state buffers on both the inputs and outputs of the flip flops, we can actually use one set of pins only.
The chip would now look like this:
the steps of writing into Memory
What happens when the programmer issues the STA instruction?
The microprocessor would turn on the WR control (WR = 0) and turn off the RD control (RD = 1).
The address is applied to the address decoder which generates a single Enable signal to turn on only one of the memory registers.
The data is then applied on the data lines and it is stored into the enabled register.
Dimensions of Memory
Memory is usually measured by two numbers: its length and its width (Length X Width).
The length is the total number of locations.
The width is the number of bits in each location.
The length (total number of locations) is a function of the number of address lines.
# of memory locations = 2( # of address lines)
So, a memory chip with 10 address lines would have
210 = 1024 locations (1K)
Looking at it from the other side, a memory chip with 4K locations would need
Log2 4096=12 address lines
The 8085 and Memory
The 8085 has 16 address lines. That means it can address
216 = 64K memory locations.
Then it will need 1 memory chip with 64 k locations, or 2 chips with 32 K in each, or 4 with 16 K each or 16 of the 4 K chips, etc.
how would we use these address lines to control the multiple chips?
Chip Select
Usually, each memory chip has a CS (Chip Select) input. The chip will only work if an active signal is applied on that input.
To allow the use of multiple chips in the make up of memory, we need to use a number of the address lines for the purpose of “chip selection”.
These address lines are decoded to generate the 2n necessary CS inputs for the memory chips to be used.
Chip Selection Example
Assume that we need to build a memory system made up of 4 of the 4 X 4 memory chips we designed earlier.
We will need to use 2 inputs and a decoder to identify which chip will be used at what time.
The resulting design would now look like the one on the following slide.
Chip Selection Example
for further detail and any query you can mail on muradalishah57@yahoo.com or can call on +923329473428,
https://www.google.com.pk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=1&cad=rja&ved=0CCwQFjAA&url=http%3A%2F%2Fen.wikipedia.org%2Fwiki%2FMicroprocessor&ei=ZXWtUveFJozN7Abq3YHQDw&usg=AFQjCNELdGXZS5JPzHDs9j6hJNdWlSLE-A&sig2=Q81X9sIqEa1ta5p6Tc37CA&bvm=bv.57967247,d.ZGU